Student loan consolidation and refinancing both combine multiple loans into one, but they serve different purposes.
Consolidation keeps federal loans together under a new federal loan, preserving benefits like income-driven repayment and forgiveness. Refinancing replaces federal or private loans with a private loan—potentially lowering your rate but sacrificing federal protections. Understanding the difference can help you pick the best option for your goals.
Table of Contents
Student loan consolidation vs. refinancing
Below is a table highlighting the crucial differences between student loan consolidation and refinancing. Keep reading for more about both.
| Feature | Consolidation | Refinance |
| Purpose | Combine federal loans into one new federal loan | Replace federal or private loans with a new private loan |
| Loan types | Federal loans only | Federal and private loans |
| Where it’s done | U.S. Department of Education | Banks, credit unions, and online lenders |
| Eligibility | Must have eligible federal loans | Based on credit score, income, and debt-to-income ratio |
| Interest rate | Weighted average of loans, rounded up to the nearest 0.125% | Determined by lender, based on credit and income |
| Federal benefits | ✔️ Yes (forgiveness, IDR plans, deferment) | ✖️ No (lose federal protections) |
| Potential savings | ✖️ No lower rate, but can extend repayment for lower monthly payments | ✔️ Possible lower interest rate and monthly payments |
| Best if you want to… | Keep federal benefits and simplify repayment | Lower your rate and reduce total repayment costs |
Student loan consolidation
How it works: To consolidate federal loans, you must apply for a Direct Consolidation Loan online through the StudentAid website or by mail. You’ll need to provide several pieces of information to complete the application, including your FSA ID and details about you, your finances, and your loans.
- Eligible loans: Most federal loans, including Direct PLUS Loans, Direct Unsubsidized Loans, Direct Subsidized Loans, and Federal Perkins Loans, are eligible for consolidation.
- Qualification requirements: You must have an eligible federal loan in good standing. If you have a student loan in default, you must make at least three successive payments before qualifying.
The following image shows how a borrower can consolidate several federal loans with a Direct Consolidation Loan:
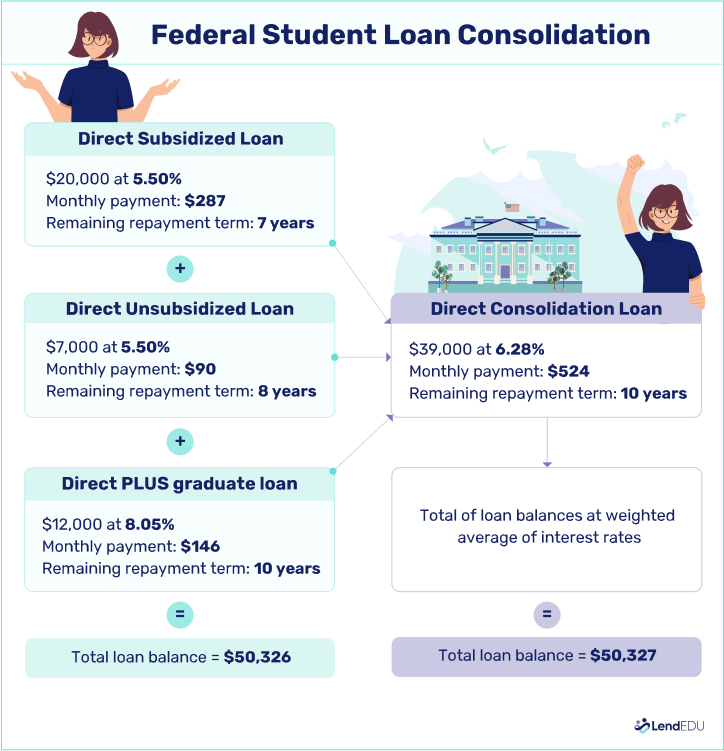
Student loan refinancing
How it works: When you refinance your student loans, you take out a new loan with a private lender to pay off your federal or private student debt.
- Eligible loans: You can refinance private and federal student loans.
- Qualification requirements: Eligibility requirements vary by lender. But when you apply, most lenders consider your credit score, income, and how much debt you have. You can also add a cosigner to your application if you need help meeting the eligibility requirements.
Here’s an example of how a borrower can refinance three private student loans into a new private loan:
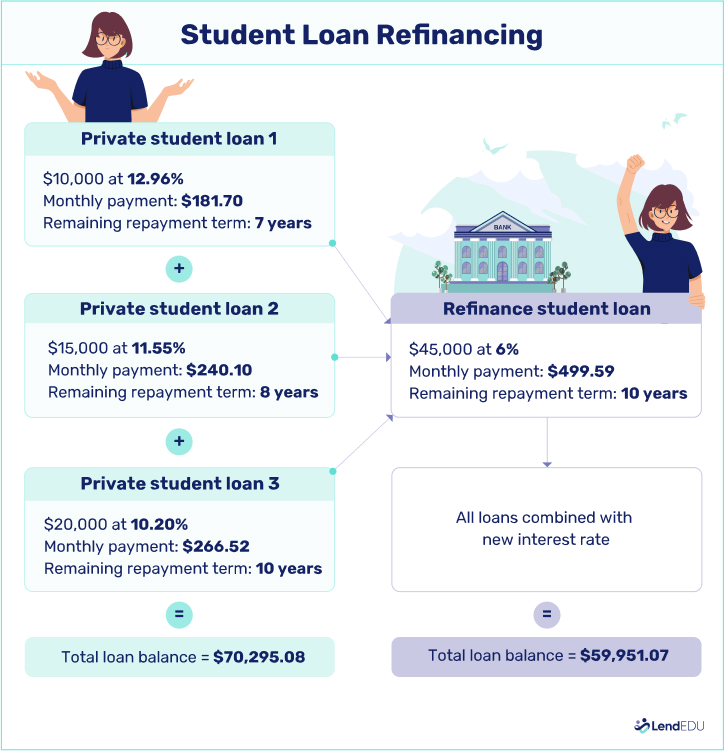
Pros and cons of consolidating vs. refinancing student loans
Before you choose federal student loan consolidation or refinancing, consider the advantages and disadvantages of both options.
The main advantage of consolidating if you have federal loans is maintaining access to federal benefits, such as student loan forgiveness programs. However, unlike refinancing, federal student loan consolidation doesn’t lower your overall rate.
| Consolidate | Refinance |
| ✅ Keep access to federal benefits | ✅ Potentially lower rate |
| ✅ Lower monthly payments | ✅ Lower monthly payments |
| ✅ No credit check required | ✅ Remove a cosigner |
| ✅ Can make debt repayment easier | ✅ Can make repayment easier |
| ❗ Doesn’t lower your overall interest rate | ❗ Lose access to federal benefits |
| ❗ You may pay more interest | ❗ Good credit required |
| ❗ Unpaid interest | ❗ Credit check required |
| ❗ Lose credit for payments made | ❗ You may not qualify for a lower rate |

Student loan consolidation does not necessarily lower the interest rate but could allow federal loans to maintain their benefits (and simplify to one payment versus multiple).
So if your overarching goal is to reduce the interest rate, refinancing is the way to go. Just be sure you understand what benefits you would give up. Refinancing can be consolidation and interest rate reduction. However, you’ll forfeit their unique benefits if the loans are federal. If your overall goal is to maintain the federal student loan benefits and simplify your life by making one payment rather than multiple, consolidation is best. Just understand that this is not a reduction in the interest rate or monthly payment.
Consolidate or refinance: Which should you do?
Whether consolidating or refinancing is best for you depends on your unique financial situation. The table below highlights when one option may be a better fit and vice versa.
| Consider consolidating if… | Consider refinancing if… |
| You want to keep access to federal benefits | You don’t plan to use your federal loan benefits |
| You want to gain access to federal benefits | You have private student loans |
| You can’t qualify for a lower rate | You have good credit and a stable income |
If you’re considering refinancing your student loans, Credible is an excellent place to start. As a marketplace, Credible lets you compare rates from multiple lenders at once, saving you time and effort. By filling out a single form, you can check your prequalified offers in minutes—without affecting your credit score.
Credible works with a variety of trusted lenders, so you can find competitive interest rates and repayment terms that fit your budget. Whether you’re refinancing to lower your rate, reduce monthly payments, or remove a cosigner, comparing options through Credible ensures you’re making an informed choice.
👉 Check your rates with Credible today to see how much you could save!

About our contributors
-
 Written by Jerry Brown, CFEI®
Written by Jerry Brown, CFEI®Jerry Brown is a freelance personal finance writer and Certified Financial Education Instructor℠ (CFEI®) who lives in New Orleans. He covers a range of personal finance topics, including credit, personal loans, and student loans.